Welcome
Our primary scientific interest lies in understanding how the brain forms percepts and uses them to make decisions, especially in the visual domain. In particular, we are interested in how the brain's perceptual beliefs about the outside world are represented by the responses of populations of cortical neurons and how their spiking activity gives rise to percepts and decisions. To that end we construct mathematical models that aim to explain neural responses and behavior.
Key concepts in the context of our work are perceptual decision-making, probabilistic inference, neural sampling, noise correlations, choice probabilities, population responses, optimal linear read-out, feedforward, recurrent and top-down processing, covert attention, psychophysical kernel, confirmation bias.
Research
Probabilistic (causal) inference and neural sampling (ongoing)
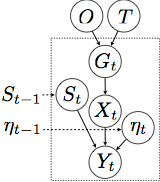 In order to draw conclusions, or inferences, about the outside world, the brain has to combine sensory information with its learnt knowledge about the structure of the external world. How this is implemented in the brain is still unknown. By generating predictions for classic perceptual tasks, we test the hypothesis that the brain performs probabilistic inference by sampling, i.e. that neuronal activity can be interpreted as samples from a generative model of the world that the brain has previously learnt.
In order to draw conclusions, or inferences, about the outside world, the brain has to combine sensory information with its learnt knowledge about the structure of the external world. How this is implemented in the brain is still unknown. By generating predictions for classic perceptual tasks, we test the hypothesis that the brain performs probabilistic inference by sampling, i.e. that neuronal activity can be interpreted as samples from a generative model of the world that the brain has previously learnt.
Lange & Haefner PLoS Comput Biol.
Haefner et al. 2016 (Neuron)
Lange & Haefner 2017 (Curr Opin Neurobiol)
Lange & Haefner 2022 (PLoS Comput Biol.)
Lange et al. 2021 (PLoS Comput Biol.)
Lange et al. 2023 (Nature Neuroscience, accepted)
Shivkumar et al. 2022 (biorxiv)
Test of model predictions using data from macaque V1.
Bondy, Haefner & Cumming 2018 (Nature Neuroscience) (pdf)
Lange et al. 2023 (JNeurophysiology)
Population (de)coding and perceptual decision-making
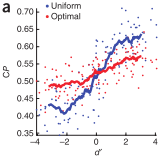 How many sensory neurons contribute to a particular decision, how are they being read out (e.g. optimal or not) and which neurons are they? We have made significant progress recently towards answering these questions by deriving the analytical relationship between noise correlations, choice probabilities and read-out weights. This will allow us to answer two of these questions as soon as multi-electrode recordings from behaving animals become available, i.e. very soon.
How many sensory neurons contribute to a particular decision, how are they being read out (e.g. optimal or not) and which neurons are they? We have made significant progress recently towards answering these questions by deriving the analytical relationship between noise correlations, choice probabilities and read-out weights. This will allow us to answer two of these questions as soon as multi-electrode recordings from behaving animals become available, i.e. very soon.
Nature Neuroscience 16, 235–242 (2013) PDF+Code+Bibtex
Applying this framework to neural recordings from MT during a dual motion direction and binocular discrimination task while area V2 was being cooled, we could constrain the origin of the noise correlations in MT.
Application to MT data allowed us to investigate the neural basis of the psychophysical suppression effect.
Liu et al. 2016 (eLife)
Chicharro D, Panzeri S, Haefner RM 2021 (elife)
Binocular vision
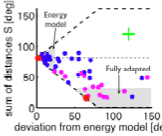 Depth perception from binocular images is an exemplary model system for studying how the brain extracts information not explicitly present in its (2D) inputs. We have been particularly interested in understanding what feedforward computations might underlie the observed neurophysiology and how much information different binocular neuron types contain about depth.
Depth perception from binocular images is an exemplary model system for studying how the brain extracts information not explicitly present in its (2D) inputs. We have been particularly interested in understanding what feedforward computations might underlie the observed neurophysiology and how much information different binocular neuron types contain about depth.
Neuron 57, vol 1, 147-158 (2008) PDF
NeurIPS 2008 PDF NeurIPS 2010 PDF
J Neuroscience, 31(22): 8295-8305 (2011) PDF
Natural image statistics
 Understanding the statistics of the natural world is important for understanding the properties of early sensory processing. Traditionally, this argument has been made in the context of efficient coding (Barlow) but what learning principle (objective function) is responsible for the properties of early sensory neurons, e.g. their receptive fields in the case of visual neurons, is still an open question and active field of research. Ultimately, this question is related to what generative model the brain has learnt for its sensory inputs.
Understanding the statistics of the natural world is important for understanding the properties of early sensory processing. Traditionally, this argument has been made in the context of efficient coding (Barlow) but what learning principle (objective function) is responsible for the properties of early sensory neurons, e.g. their receptive fields in the case of visual neurons, is still an open question and active field of research. Ultimately, this question is related to what generative model the brain has learnt for its sensory inputs.
PLoS Comput Biol 10(3): e1003468
People

VSS 2022
Lab Members

Ralf Haefner, PI
Biography

Anton Pletenev, Graduate Student

Xinyi Yuan, Graduate Student

2019
Alumni
- Samuel Alvernaz
- Himanshu Ahuja
- Garrett Bunce, Undergraduate researcher, now PhD student at U Maryland
- Ankani Chattoraj, Graduate student, now Data Science Engineer, Autonomous Vehicle Behavior Test
- Zhen Chen, Graduate student
- Nicholas Cimaczevski , Undergraduate researcher, now PhD student at MPI/University of Tübingen
- Matthew Hochberg, Undergraduate researcher
- Sunny Jin , CVS summer researcher, now Master in Psychology, Istanbul, Turkey
- Jovan Kemp, CVS summer student, now PhD student at Brown
- Richard Lange, Graduate student, now faculty member at RIT
- Gabor Lengyel, Postdoc
- Ruolan (Leslie) Li, Undergraduate researcher, now PhD student at University of Maryland
- Shizhao Liu
- Joseph Majesky, Undergraduate researcher
- Katherine Moon, now undergraduate at Yale University
- Katarina Nichols, now PhD student at University of Rochester
- Boris Penaloza, Postdoc
- Yong Soo Ra, now PhD student at Harvard University
- Sabya Shivkumar, now postdoc at Columbia University
- Martynas Snarskis, Undergraduate researcher, now lab manager in the lab of David Gallo at University of Chicago
- Xuan Wen, Undergraduate researcher, now PhD student at Vanderbuilt University
- Shuchen Wu, now PhD student at MPI Tübingen
- Linghao Xu, Graduate student, now PhD student in the lab of Ruben Coen-Cagli at Einstein College of Medicine
- Ziyi Zhu, Undergraduate researcher, now PhD student at Columbia University
Collaborators
Experimental labs
- Rick Born
- Bruce Cumming
- Greg DeAngelis
- Jude Mitchell
- Hendrikje Nienborg
- Chris Pack
- John Reynolds
- Adam Snyder
Theoretical labs
Publications
- Benjamin Peters, Gunnar Blohm, Ralf Haefner, Leyla Isik, Nikolaus Kriegeskorte, Jennifer S. Lieberman, Carlos R. Ponce, Gemma Roig, Megan A.K. Peters. Generative adversarial collaborations: a new model of scientific discourse. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, Volume 29, Issue 1, 2025, Pages 1-4, ISSN 1364-6613, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2024.10.015.
- Penaloza B, Shivkumar S, Lengyel G, DeAngelis GC, Haefner RM. Causal inference predicts the transition from integration to segmentation in motion perception. Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 12;14(1):27704. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78820-6. PMID: 39533022; PMCID: PMC11558006.
- Haefner, R.M., Beck, J., Savin, C. et al. How does the brain compute with probabilities? arXiv:2409.02709; doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2409.02709
- Lange, R.D., Shivkumar, S., Chattoraj, A. et al. Bayesian encoding and decoding as distinct perspectives on neural coding. Nat Neurosci 26, 2063–2072 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-023-01458-6
- Shivkumar S, DeAngelis GC, Haefner RM. Hierarchical motion perception as causal inference. bioRxiv 2023.11.18.567582; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.18.567582
- Fu J, Shrinivasan S, Ponder K, Muhammad T, Ding Z, Wang E, Ding Z, Tran DT, Fahey PG, Papadopoulos S, Patel S, Reimer J, Ecker AS, Pitkow X, Haefner RM, Sinz FH, Franke K, Tolias AS. Pattern completion and disruption characterize contextual modulation in mouse visual cortex. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 14:2023.03.13.532473. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.13.532473. PMID: 36993321; PMCID: PMC10054952.
- Lange RD, Gomez-Laberge C, Berezovskii VK, Plenetev A, Sherdil A, Hartmann T, Haefner RM, Born RT. Weak Evidence for Neural Correlates of Task-Switching in Macaque V1. J Neurophysiol. 2023 Mar 22. doi: 10.1152/jn.00085.2022. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36947884.
- Noel JP, Shivkumar S, Dokka K, Haefner RM, Angelaki DE. Aberrant causal inference and presence of a compensatory mechanism in autism spectrum disorder. Elife. 2022 May 17;11:e71866. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71866. PMID: 35579424; PMCID: PMC9170250.
- Shivkumar S, Cappelloni MS, Maddox RK, Haefner RM. Inferring sources of suboptimality in perceptual decision making using a causal inference task. bioRxiv 2022.04.28.489925; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.28.489925
- Lange RD, Haefner RM. Task-induced neural covariability as a signature of approximate Bayesian learning and inference. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Mar 8;18(3):e1009557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009557.
- Lange RD, Chattoraj A, Beck J, Yates J, Haefner R. A confirmation bias in perceptual decision-making due to hierarchical approximate inference, PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Nov 29;17(11):e1009517. | pdf
- Lange, R., Shivkumar, S., Chattoraj, A., and Haefner, R. 2021. Bayesian Encoding and Decoding as Distinct Perspectives on Neural Coding. bioRxiv, p.2020–10. | biorxiv
- Chattoraj, A., Shivkumar, S., Ra, Y., and Haefner, R. 2021. A confirmation bias due to approximate active inference. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society. | Abstract | pdf
- Chattoraj, A., Snarskis, M., and Haefner, R. 2021. Relating confidence judgements to temporal biases in perceptual decision-making. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society. | Abstract | pdf
- Chicharro D, Panzeri S, Haefner RM. Stimulus-dependent relationships between behavioral choice and sensory neural responses. Elife. 2021 Apr 7;10:e54858. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54858.
- Cappelloni MS, Shivkumar S, Haefner RM, Maddox RK. Task-uninformative visual stimuli improve auditory spatial discrimination in humans but not the ideal observer. PLoS One. 2019 Sep 9;14(9):e0215417. | article
- Shivkumar S, Lange L, Chattoraj A, Haefner R. A probabilistic population code based on neural samples, NeurIPS 2018. | article
- Kawaguchi K, Clery S, Pourriahi P, Seillier L, Haefner R, Nienborg H. Using confidence inferred from pupil-size to dissect perceptual task-strategy: support for a bounded decision-formation process, Journal of Neuroscience 2018, 38 (41) 8874-8888. | article
- Bondy AG, Haefner RM & Cumming BG. Feedback determines the structure of correlated variability in primary visual cortex. Nature Neuroscience. 2018 Feb. | pdf
- Lange RD, Haefner RM. Characterizing and interpreting the influence of internal variables on sensory activity. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017 Aug 22;46:84-89. | article
- Chicharro, D., Panzeri, S., and Haefner, R.M. Choice Probabilities in the presence of nonzero signal stimuli, internal bias, and decision feedback, bioRxiv. | article
- Lange, R.D. and Haefner, R.M. Inferring the brain’s internal model from sensory responses in a probabilistic inference framework, bioRxiv. | article
- Liu LD, Haefner RM, Pack CC (2016). A neural basis for the spatial suppression of visual motion perception, elife. | article
- Haefner RM, Berkes P, Fiser J (2016). Perceptual Decision-Making as Probabilistic Inference by Neural Sampling. Neuron, 90(3):649-60. | article
- Smolyanskaya A, Haefner RM, Lomber SG, Born RT (2015). A Modality-Specific Feedforward Component of Choice-Related Activity in MT. Neuron, 87(1):208-19. | article
- Lies, Häfner & Bethge (2014). Slow Subspace Analysis: A new Algorithm for Invariance Learning, PLoS Computational Biology 10(3):e1003468 | article
- Haefner, R. M., Gerwinn, S., Macke, J. H., & Bethge, M. (2013). Inferring decoding strategies from choice probabilities in the presence of correlated variability. Nature Neuroscience, 16(2), 235–242. doi:10.1038/nn.3309 | article
- Haefner & Bethge (2010). Evaluating neural codes for inference using Fisher Information, Advances in Information Processing Systems 23, 1993-2001. | pdf
- Tanabe, Haefner & Cumming (2010). Push-pull organization of binocular receptive fields robustly encodes disparity in monkey V1, Journal for Neuroscience 31, 22, 8295-8305. | pdf
- Haefner & Cumming (2008). An improved estimator of Variance Explained in the presence of noise, Advances in Information Processing Systems 21, 585-592. | article
- Haefner & Cumming (2008). A specialization for the statistics of binocular images in primate V1, Neuron 57, 147-156. | pdf
- Häfner, Evans, Dehnen & Binney (2000). A dynamical model of the inner Galaxy, Monthly Notes of the Royal Astronomical Society 314, 433. | pdf
- Häfner, Evans, Dehnen & Binney (1999). A dynamical model of the inner Galaxy in "Galaxy Dynamics: A Rutgers Symposium", Eds. Merrit, Sellwood, Valluri, 371. | article
- Evans, Häfner & De Zeeuw (1997). Simple three-integral scale-free galaxy models, Monthly Notes of the Royal Astronomical Society 268, 328. | pdf
Lab Conference Presentations
- A. Pletenev, S. Liu, R.M. Haefner, A.C. Snyder (2023). Noise correlations and choice probabilities during learning and task switching in V4. SfN 23 | Abstract.
- Gabor Lengyel, Sabyasachi Shivkumar & Ralf M. Haefner (2023). A General Method for Testing Bayesian Model Using Neural Data. COSYNE23, Montreal, QC | Abstract (pdf).
- Boris Penaloza, Sabyasachi Shivkumar, Gabor Lengyel, Linghao Xu, Gregory C. DeAngelis & Ralf M. Haefner (2023). Divisive normalization as a mechanism for hierarchical causal inference in motion perception. COSYNE23, Montreal, QC | Abstract (pdf).
- Sabyasachi Shivkumar, Zhexin Xu, Gabor Lengyel, Gregory C. DeAngelis & Ralf M. Haefner (2022). Causal inference explains hierarchical motion perception and is reflected in neural responses in MT. COSYNE22, Lisbon, Portugal | Abstract (pdf).
- X Wen, A Chattoraj, R Haefner (2022). Investigating limits and time scales of a perceptual confirmation bias. VSS | Abstract.
- RM Haefner, S Shivkumar, A Chattoraj, YS Ra (2022). Eye-movements during active sensing suffer from a confirmation bias. VSS | Abstract.
- Y Lin, Z Chen, R Haefner, D Tadin (2022). Moving toward a unifying framework for perceptual decision making that combines threshold and reaction time approaches. VSS | Abstract.
- A Chattoraj, M Snarskis, A Zylberberg, R Haefner (2022). Perceptual confirmation bias induces overconfidence in addition to a primacy bias during evidence integration. VSS | Abstract.
- S Shivkumar, B Penaloza, G Lengyel, GC DeAngelis, RM Haefner (2022). Causal inference underlies hierarchical motion perception. VSS | Abstract.
- Chattoraj, Shivkumar, Ra, Moon, Haefner (2020). A confirmation bias on how humans actively sample sensory information. VSS | Abstract.
- Chattoraj, Lange, Haefner (2020). Using the perceptual confirmation-bias to study learning and feedback in fovea and periphery. VSS | Abstract.
- Shivkumar, DeAngelis, Haefner (2020). A causal inference model for the perception of complex motion in the presence of self-motion. VSS | Abstract.
- Shivkumar, DeAngelis & Haefner (2019). A causal inference model for the perception of complex motion in the presence of self-motion. CCN | Abstract.
- Chattoraj, Lange, Wu, Haefner (2019). A neural-sampling based model of early visual processing based on leaky integrate-and-fire neurons. Bernstein | Abstract.
- Chattoraj, Lange & Haefner (2019). Using the perceptual confirmation-bias to study learning and feedback in fovea and periphery. CCN | Abstract.
- Shivkumar, Cappelloni, Maddox, Haefner (2019). Approximate causal inference based cue integration. Bernstein | Abstract
- Shivkumar, Cappelloni, Maddox, Haefner (2018). Approximate inference explains paradoxical data in two-event causal inference task. CCN | Abstract.
- Lange, Chattoraj, Hochberg, Beck, Yates, Haefner (2018). A perceptual confirmation bias from approximate online inference. CCN | Abstract.
- Lange, Gomez-Laberge, Haefner, Born (2018). Neural signatures of variable beliefs increase with task learning in V1. AREADNE | pdf
- Cappelloni, Shivkumar, Haefner & Maddox (2018). A Pair of Ambiguous Visual Stimuli Improves Auditory Spatial Discrimination. International Multisensory Research Forum.
- Lange, Bondy, Cumming & Haefner (2018). Within-trial dynamics of noise correlations imply binarized feedback of internal beliefs. Cosyne.
- Chattoraj, Wu, Lange & Haefner (2018). A probabilistic population code based on neural sampling. Cosyne
- Kawaguchi, Haefner, Nienborg (2017). Evaluating perceptual strategy using decision confidence inferred from pupil size in macaques. SfN.
- Lange, Chattoraj, Hochberg, Yates & Haefner (2017). Perceptual confirmation bias from approximate online inference. Bernstein
- Lange, Chattoraj, Hochberg, Yates (2017). Confirmation bias from approximate online inference. Cosyne.
- Chicharro, Panzeri & Haefner (2016). Choice probabilities in the presence of nonzero signal stimuli, internal bias, and decision feedback. Cosyne
- Lange, Bondy, Cumming & Haefner (2016). On the neural basis of probabilistic inference during perceptual decision making. Cosyne.
- Haefner (2015). Choice probabilities,in a feedforward perceptual decision- making framework with multiple neuronal input populations. Cosyne
- Haefner (2014). On the relationship between stimulus-evoked and choice-related responses and correlations during perceptual decision-making in a probabilistic inference framework. SfN | Abstract.
Resources
Bernstein Meeting 2017: Satellite workshop on Neural sampling
Contact
Department for Brain & Cognitive Sciences
358 Meliora Hall, Box 270268
University of Rochester
Rochester, NY 14627-0268
email:
News
- New publication: "Generative adversarial collaborations: a new model of scientific discourse"
- New publication (SciReports 2024): "Causal inference predicts the transition from integration to segmentation in motion perception"
- New preprint on how the brain computes with probabilities
- New publication (NatNeuro 2023): "Bayesian encoding and decoding as distinct perspectives on neural coding"
- New SfN Abstract: "Noise correlations and choice probabilities during learning and task switching in V4”
- New NeurIPS workshop paper (pdf): "A General Method for Testing Bayesian Models using Neural Data”
- Congratulations to lab alumnus Richard Lange, who has become a faculty member at RIT
- New preprint: "Hierarchical motion processing as causal inference"
- New preprint: "Pattern completion and disruption characterize contextual modulation in mouse visual cortex"
- New publication (JNeurophysiology): "Weak Evidence for Neural Correlates of Task-Switching in Macaque V1"
- New publication (eLife): "Aberrant causal inference and presence of a compensatory mechanism in autism spectrum disorder"
- New preprint: "Inferring sources of suboptimality in perceptual decision making using a causal inference task"
- New publication (PLoS CB): "Task-induced neural covariability as a signature of approximate Bayesian learning and inference"
- New publication (PLoS CB): "A confirmation bias in perceptual decision-making due to hierarchical approximate inference"
- New publication: "A confirmation bias due to approximate active inference"
- New publication: "Relating confidence judgements to temporal biases in perceptual decision-making"
- New publication (eLife): "Stimulus-dependent relationships between behavioral choice and sensory neural responses"
- Talk in Bernstein workshop on dynamic probabilistic inference in the brain
- A team of researchers at the University of Rochester, including Greg DeAngelis, the George Eastman Professor of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, and Ralf Haefner, an assistant professor of brain and cognitive sciences, received a $12.2 million grant award from the National Institutes of Health for a project to better understand how the brain uses causal inference to distinguish self-motion from object motion. Read More...
- VSS 2020 talk: A causal inference model for the perception of complex motion in the presence of self-motion by Sabyasachi Shivkumar, Gregory DeAngelis, Ralf Haefner
- VSS 2020 Poster: A confirmation bias on how humans actively sample sensory information by Ankani Chattoraj, Sabyasachi Shivkumar, Ra Yong Soo, Katherine Moon, Ralf Haefner
- VSS 2020 Poster: on Using the perceptual confirmation-bias to study learning and feedback in fovea and periphery by Ankani Chattoraj, Richard D Lange, Ralf M Haefner
- Bernstein 2019 poster: Approximate causal inference based cue integration by Sabyasachi Shivkumar, Madeline Cappelloni, Ross Maddox, Ralf M. Haefner
- Bernstein 2019 poster: A neural-sampling based model of early visual processing based on leaky integrate-and-fire neurons by Ankani Chattoraj, Richard Lange, Suchen Wu, Ralf Haefner
- CCN 2019 poster: A causal inference model for the perception of complex motion in the presence of self-motion by Sabyasachi Shivkumar, Gregory DeAngelis, Ralf Haefner
- CCN 2019 poster: Using the perceptual confirmation-bias to study learning and feedback in fovea and periphery by Ankani Chattoraj, Richard Lange, Ralf Haefner
- New publication: "Task-uninformative visual stimuli improve auditory spatial discrimination in humans but not the ideal observer"
- Nov 14: Invited Theory Center seminar at Duke University
- Sep 12: Invited talk at Center for Vision Research, York University
- CCN 2018 poster: Approximate inference explains paradoxical data in two-event causal inference task by Sabyasachi Shivkumar, Madeline Cappelloni, Ross Maddox, Ralf M. Haefner
- CCN 2018 poster: A perceptual confirmation bias from approximate online inference by Richard Lange, Ankani Chattoraj, Matthew Hochberg, Jeffrey Beck, Jacob Yates, Ralf Haefner
- New pre-print: "A confirmation bias in perceptual decision-making due to hierarchical approximate inference"
- NeurIPS 2018 Talk: "A probabilistic population code based on neural samples"
- AREADNE 2018 poster (pdf): "Neural signatures of variable beliefs increase with task learning in V1"
- Cosyne poster: III-89. "A probabilistic population code based on neural sampling" (Sat)
- Cosyne poster: II-18. "Within-trial dynamics of noise correlations imply binarized feedback of internal beliefs" (Fri)
- Paper out in Nature Neuroscience: "Feedback determines the structure of correlated variability in primary visual cortex"
- New pre-print: "Using confidence inferred from pupil-size to dissect perceptual task-strategy: support for a bounded decision-formation process"
- Colloquium at Tufts
- Seminar talk (pdf) at Baylor College of Medicine
- SfN 2017 poster: Evaluating perceptual strategy using decision confidence inferred from pupil size in macaques by Kawaguchi, Haefner, Nienborg
- Bernstein 2017 poster: Perceptual confirmation bias from approximate online inference by Lange, Chattoraj, Hochberg, Yates & Haefner
- Bernstein Meeting: Workshop on Neural sampling
- Paper out in Current Opinion in Neurobiology: "Characterizing and interpreting the influence of internal variables on sensory activity"
- New pre-print on "Decision-Related Signals In The Presence Of Nonzero Signal Stimuli, Internal Bias, And Feedback" with Daniel Chicharro and Stefano Panzeri.
- New preprint on “Characterizing the influence of 'internal states' on sensory activity
- Cosyne 2017: Poster on "Perceptual confirmation biases from approximate online inference"
- New pre-print on "Inferring the brain's internal model from sensory responses in a probabilistic inference framework"
- Poster at AREADNE: "Top-down attention in a probabilistic inference framework" in collaboration with Pietro Berkes and Josef Fiser.
- Paper out in eLife: "A neural basis for the spatial suppression of visual motion perception" in collaboration with Dave Liu and Chris Pack.
- Paper out in Neuron: "The implications of perception as probabilistic inference for correlated neural variability during behavior" in collaboration with Pietro Berkes and Jozsef Fiser.
- Spring School: "The role of simulations in neuroscience". Co-organized and co-taught a week-long seminar on the philosophy & science of simulations together with Philipp Berens & Eckhart Arnold, including visits to HBP co-director Felix Schürmann and chief critic Alex Pouget.
- Paper accepted at Neuron: "The implications of perception as probabilistic inference for correlated neural variability during behavior" in collaboration with Pietro Berkes and Jozsef Fiser: http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.0257
- Cosyne 2016
Two posters accepted
Invited Talk in workshop on "Form and function of choice-related feedback signals in decision making" - New paper: "A modality-specific feedforward component of choice-related activity in MT" in collaboration with Alexandra Smolyanskaya, Stephen G. Lomber and Richard T. Born (Neuron)
- 2015, June 10-11: Bernstein SPARKS workshop on Deep Learning & Brain
- Cosyne 2015
Poster on "Choice probabilities, detect probabilities, and read-out with multiple neuronal input populations"
Workshop Talk on "The source of sensory & decision-related activity in area MT" - SfN 2014
Poster on "On the relationship between stimulus-evoked and choice-related responses and correlations during perceptual decision-making in a probabilistic inference framework" -
New job at the Department for Brain & Cognitive Sciences, University of Rochester (NY)
In Sept 2014 moved to Rochester and started my own group as an assistant professor.
